The Future of Electric Vehicles: Advancements in Battery Technology and Charging Infrastructure
Electric vehicles (EVs) have been around for more than a century, but their popularity has only recently begun to soar. As a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to gasoline-powered cars, EVs offer numerous advantages, such as zero emissions, lower operating costs, and a quieter ride. However, two key challenges have hampered the widespread adoption of EVs: limited driving range and inadequate charging infrastructure. Fortunately, advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure are set to transform the future of electric vehicles.
Battery Technology: The Key to Longer Driving Range
The driving range of an EV refers to the distance it can travel on a single charge. While most EVs can cover around 100-200 miles on a single charge, this falls short of the range offered by gasoline-powered cars. However, the latest battery technologies are set to change this. One promising technology is solid-state batteries, which use a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid or gel electrolytes used in current lithium-ion batteries. Solid-state batteries offer several advantages over traditional batteries, such as higher energy density, faster charging times, and improved safety.
Battery technology and charging infrastructure
Another technology that could revolutionize battery technology is lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries. Li-S batteries use sulfur as the cathode material, which is cheaper, more abundant, and less toxic than the cobalt and nickel used in lithium-ion batteries. Li-S batteries have a higher energy density than lithium-ion batteries, which means they can store more energy and offer longer driving range. In addition, Li-S batteries are lighter and more compact than lithium-ion batteries, which could reduce the weight of EVs and improve their efficiency.
Charging Infrastructure: The Key to Convenience and Accessibility
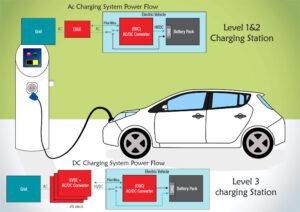
The second challenge facing the widespread adoption of EVs is the lack of charging infrastructure. While gasoline-powered cars can be refueled at thousands of gas stations around the world, EVs require specialized charging stations that are not yet widely available. However, this is changing rapidly. Governments, automakers, and energy companies are investing heavily in charging infrastructure, with the aim of making EV charging as convenient and accessible as refueling a gasoline-powered car.
One type of charging station that is becoming increasingly popular is the fast charger. Fast chargers use high-powered DC (direct current) electricity to quickly recharge an EV’s battery. Depending on the battery capacity and charging rate, a fast charger can recharge an EV’s battery from 0-80% in around 30-60 minutes. Fast chargers are typically located along major highways, in shopping malls, and at other public locations where drivers are likely to spend time.
Another type of charging station that is gaining popularity is the home charger. Home chargers allow EV owners to recharge their vehicles overnight, using the standard AC (alternating current) electricity supplied by their homes. Home chargers can be installed in garages or driveways, providing EV owners with the convenience of recharging their vehicles at home, just like they would charge their smartphones or laptops.
Importance of Electric Vehicles
Finally, wireless charging is another technology that could transform EV charging. Wireless charging uses magnetic induction to transfer electricity from a charging pad on the ground to a receiver on the bottom of an EV. Wireless charging would eliminate the need for cables and plugs, making charging even more convenient and accessible. While wireless charging is still in the early stages of development, it has the potential to revolutionize the way we charge our EVs.
The Future of Electric Vehicles: Cleaner, Smarter, and More Convenient
Advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure are set to transform the future of electric vehicles. As battery technology continues to improve, EVs will be able to offer longer driving range, faster charging times, and improved safety. Meanwhile, the growing network of charging infrastructure will
make charging an EV as convenient and accessible as refueling a gasoline-powered car. This will enable more drivers to make the switch to electric, which will result in a cleaner, more sustainable future.
The benefits of electric vehicles are clear. They emit zero tailpipe emissions, which means they don’t contribute to air pollution or climate change. They are also more efficient than gasoline-powered cars, which means they require less energy to travel the same distance. This translates into lower operating costs for EV owners, as they spend less money on fuel and maintenance. Finally, EVs offer a quieter, more comfortable ride, which can improve the driving experience for many drivers.
However, despite these benefits, EVs have not yet become mainstream. One of the main reasons for this is the limited driving range of most EVs. While some models can cover more than 300 miles on a single charge, most EVs can only cover around 100-200 miles. This means that EVs are not yet suitable for long-distance travel, which limits their appeal to many drivers.
Fortunately, advancements in battery technology are set to change this. Solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur batteries offer higher energy density than current lithium-ion batteries, which means they can store more energy and offer longer driving range. In addition, these batteries are safer, more compact, and lighter than current batteries, which could improve the performance and efficiency of EVs.
Solid-state batteries are an especially promising technology. They use a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid or gel electrolytes used in current lithium-ion batteries. This offers several advantages, such as higher energy density, faster charging times, and improved safety. Solid-state batteries can also operate at higher temperatures, which makes them more suitable for use in electric vehicles. However, solid-state batteries are still in the early stages of development, and it may be several years before they are commercially available.
Lithium-sulfur batteries are another technology that could revolutionize battery technology. They use sulfur as the cathode material, which is cheaper, more abundant, and less toxic than the cobalt and nickel used in lithium-ion batteries. Li-S batteries have a higher energy density than lithium-ion batteries, which means they can store more energy and offer longer driving range. In addition, Li-S batteries are lighter and more compact than lithium-ion batteries, which could reduce the weight of EVs and improve their efficiency.
Advancements in battery technology will also improve the safety of EVs. Lithium-ion batteries are prone to thermal runaway, which can lead to fires and explosions. However, solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur batteries are less prone to thermal runaway, which makes them safer for use in electric vehicles. In addition, advancements in battery management systems will allow EV manufacturers to monitor the temperature and voltage of batteries more closely, which will improve the safety and reliability of EVs.
While advancements in battery technology are critical to the future of electric vehicles, charging infrastructure is equally important. EVs require specialized charging stations that are not yet widely available. However, this is changing rapidly. Governments, automakers, and energy companies are investing heavily in charging infrastructure, with the aim of making EV charging as convenient and accessible as refueling a gasoline-powered car.
Fast chargers are becoming increasingly popular as a type of charging station. They use high-powered DC (direct current) electricity to quickly recharge an EV’s battery. Depending on the battery capacity and charging rate, a fast charger can recharge an EV’s battery from 0-80% in around 30-60 minutes. Fast chargers are typically located along major highways, in shopping malls, and at other public locations where drivers are likely to spend time.
Conclusion
Home chargers are another type of charging station that is gaining popularity. Home chargers allow EV owners to recharge their vehicles overnight